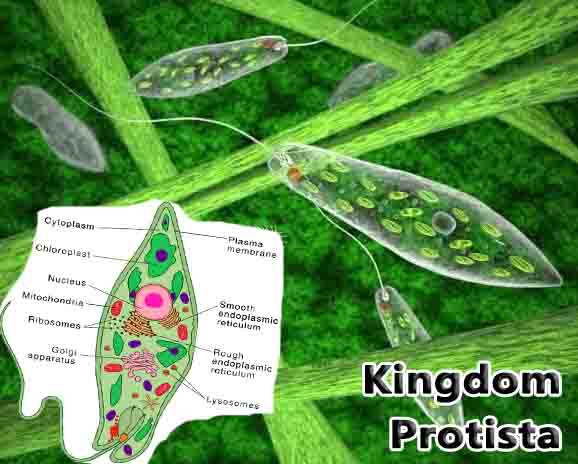
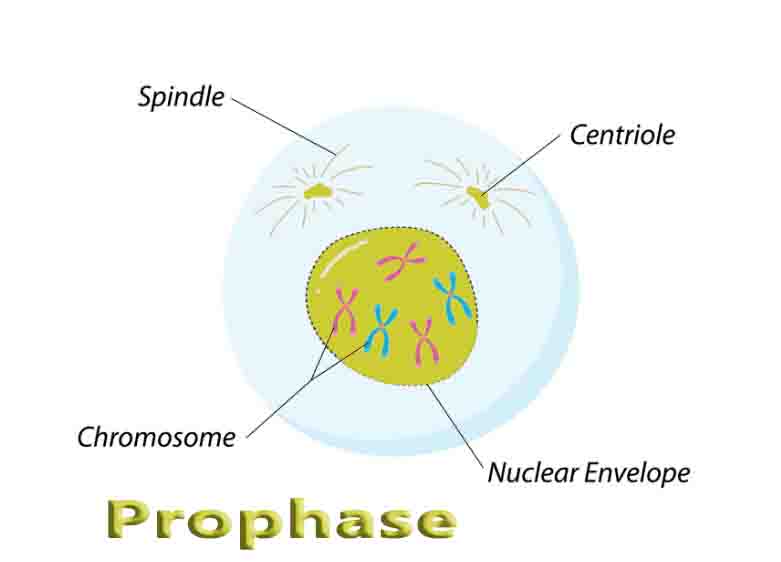
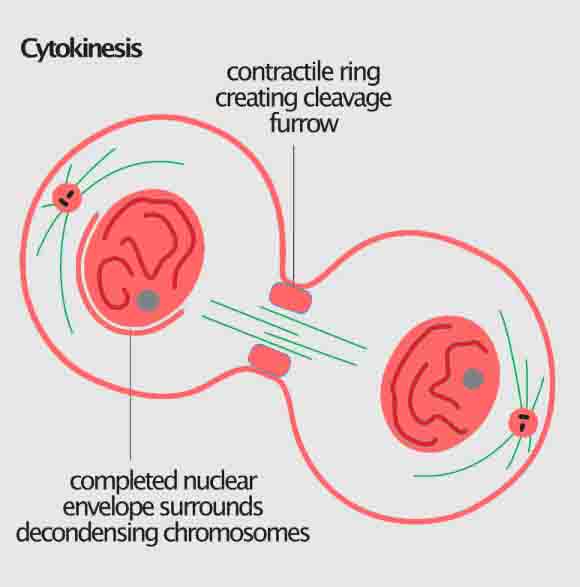
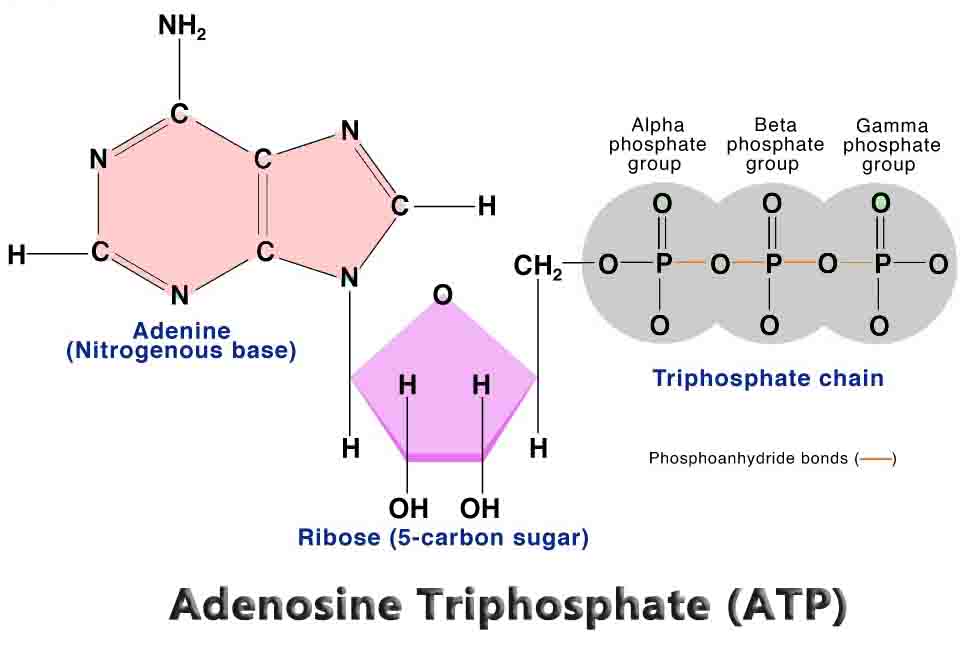
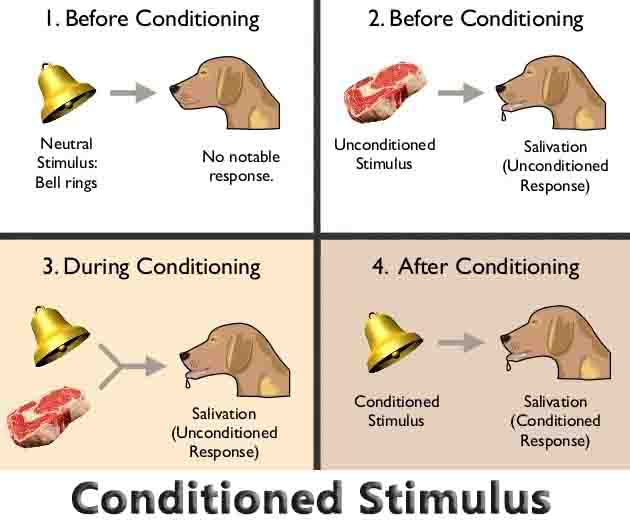
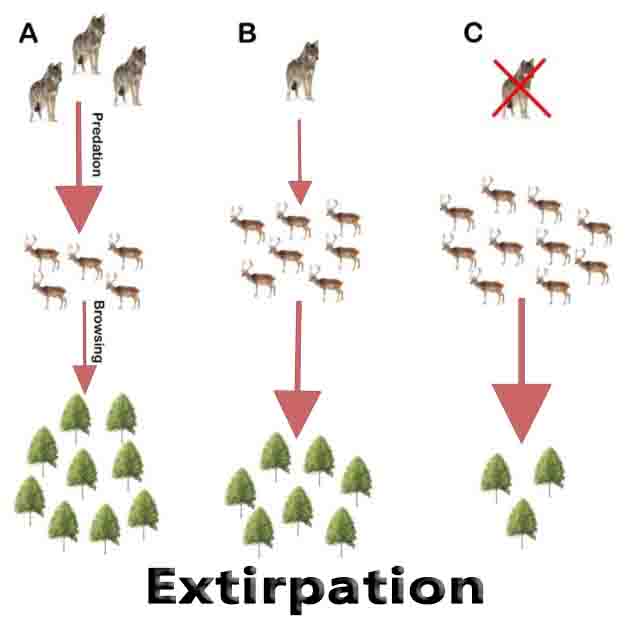
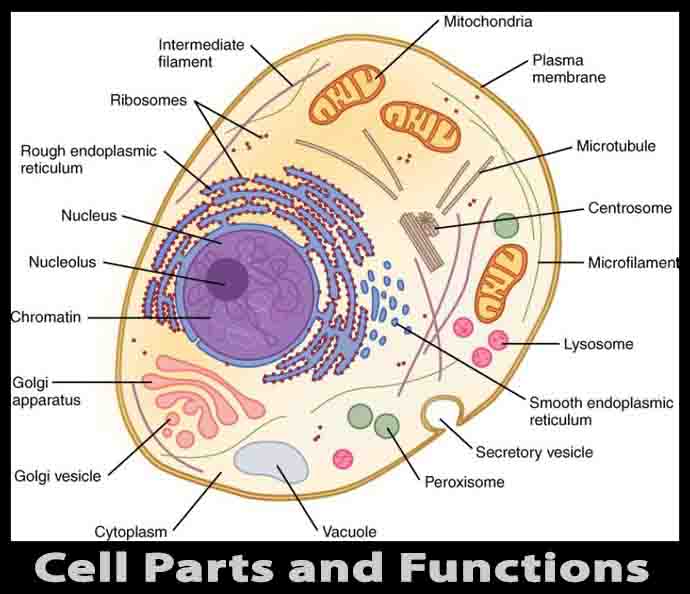
Fungi
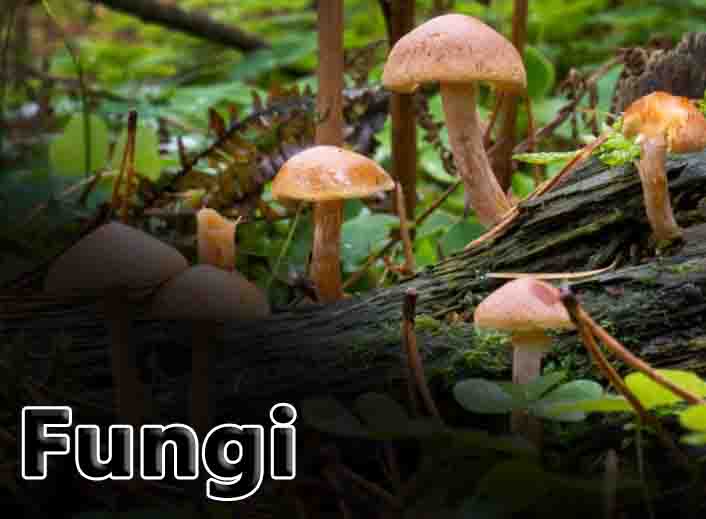
Fungi Definition Fungi (singular: fungus) are a kingdom of usually multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophs (cannot make their own food) and have important roles in nutrient cycling in an ecosystem. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually, and they also have symbiotic associations with plants and bacteria. However, they are also responsible for some diseases … Read more